Abstract
Background: New prognostic factors have been recently identified in AML patient population that include frequent mutations of receptor tyrosine kinases (RTK) including KIT, PDGFR, FLT3, that are associated with higher risk of relapse. Thus, targeting RTKs could improve the therapeutic outcome in AML patients.
Aim: To create a digital drug model for dasatinib and validate the predicted response in AML patient samples with ex vivo drug sensitivity testing.
Methods: The Beat AML project (supported by the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society) collects clinical data and bone marrow specimens from AML patients. Bone marrow samples are analyzed by conventional cytogenetics, whole-exome sequencing, RNA-seq, and an ex vivo drug sensitivity assay. For 50 randomly chosen patients, every available genomic abnormality was inputted into a computational biology program (Cell Works Group Inc.) that uses PubMed and other online resources to generate patient-specific protein network maps of activated and inactivated pathways. Digital drug simulations with dasatinib were conducted by quantitatively measuring drug effect on a composite AML disease inhibition score (DIS) (i.e., cell proliferation, viability, and apoptosis). Drug response was determined based on a DIS threshold reduction of > 65%. Computational predictions of drug response were compared to dasatinib IC50 values from the Beat AML ex vivo testing.
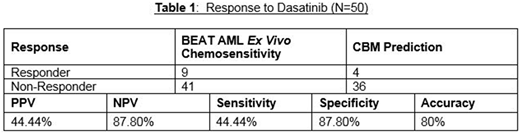
Results: 23/50 (46%) AML patients had somatic mutations in an RTK gene (KIT, PDGFR, FLT3 (ITD (n=15) & TKD (n=4)), while 27/50 (54%) were wild type (WT) for the RTK genes. Dasatinib showed ex vivo cytotoxicity in 9/50 (18%) AML patients and was predicted by CBM to remit AML in 9/50 AML patients with 4 true responders and 5 false positive. Ex vivo dasatinib responses were correctly matched to the CBM prediction in 40/50 (80%) of patients (Table1), with 10 mismatches due to lack of sufficient genomic information resulting in profile creation issues and absence of sensitive loops in the profile. Only 4/23 (17%) RTK-mutant patients and 5/27(19%) RTK-WT patients were sensitive to dasatinib ex vivo, indicating that presence of somatic RTK gene mutations may not be essential for leukemia regression in response to dasatinib. Co-occurrence of mutations in NRAS, KRAS and NF1 seemed to associate with resistance as seen in 10 of the 14 profiles harboring these mutations.
Conclusion: Computational biology modeling can be used to simulate dasatinib drug response in AML with high accuracy to ex vivo chemosensitivity. DNA mutations in RTK genes may not be required for dasatinib response in AML. Co-occurrence of NRAS, KRAS and NF1gene mutations may be important co-factors in modulating response to dasatinib.
Tyner:Leap Oncology: Equity Ownership; Syros: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; Gilead: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Research Funding; Aptose: Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding; Agios: Research Funding. Druker:Third Coast Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Millipore: Patents & Royalties; Vivid Biosciences: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Oregon Health & Science University: Patents & Royalties; McGraw Hill: Patents & Royalties; Celgene: Consultancy; MolecularMD: Consultancy, Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; GRAIL: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol-Meyers Squibb: Research Funding; Amgen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Aptose Therapeutics: Consultancy, Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Henry Stewart Talks: Patents & Royalties; Patient True Talk: Consultancy; Blueprint Medicines: Consultancy, Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; ARIAD: Research Funding; Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center: Research Funding; Beta Cat: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Cepheid: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Leukemia & Lymphoma Society: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; ALLCRON: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Aileron Therapeutics: Consultancy; Gilead Sciences: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Monojul: Consultancy. Sahu:Cellworks Research India Private Limited: Employment. Vidva:Cellworks Research India Private Limited: Employment. Kapoor:Cellworks Research India Private Limited: Employment. Azam:Cellworks Research India Private Limited: Employment. Kumar:Cellworks Research India Private Limited: Employment. Chickdipatti:Cellworks Research India Private Limited: Employment. Raveendaran:Cellworks Research India Private Limited: Employment. Gopi:Cellworks Research India Private Limited: Employment. Abbasi:Cell Works Group Inc.: Employment. Vali:Cell Works Group Inc.: Employment. Cogle:Celgene: Other: Steering Committee Member of Connect MDS/AML Registry.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal